
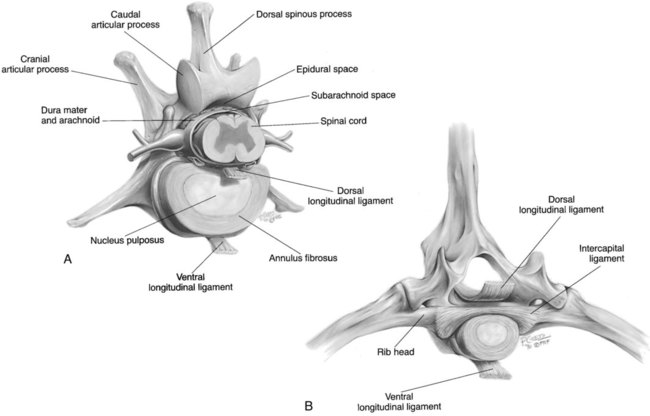
They are formed between superior and inferior articular facets. Its main function is to prevent posterior herniation of the intervertebral discs.Īdjacent vertebral arches are connected by synovial joints called zygapophyseal (facet) joints. The posterior longitudinal ligament runs inside the vertebral canal along the posterior surface of the vertebral bodies, from C2 to the sacrum. Its role is to limit extension and prevent hyperflexion of the spine. The anterior longitudinal ligament extends along the exterior, anterolateral aspect of the vertebral bodies from the base of the skull to the sacrum. The vertebral bodies and intervertebral discs are reinforced by two fibrous, longitudinal ligaments. The vertebral bodies of the cervical vertebrae are also interconnected by uncovertebral joints (clefts of Luschka). The lumbar spine is the most susceptible to disc herniations due to its location and significant involvement in weight bearing. Their role is to serve as shock absorbers, prevent friction and permit a small degree of flexibility between vertebrae. Intervertebral discs are composed of a fibrous outer ring ( annulus fibrosus) that surrounds a gelatinous nucleus ( nucleus pulposus). The exceptions are C1-C2 and after S2, where such symphyses do not exist. Adjacent vertebral bodies are joined by symphyses called intervertebral symphyses (discs). Intervertebral fibrocartilage, Fibrocartilago intervertebralisĪfter learning about individual vertebrae, it’s time to explore how the vertebral column is kept together as a unit. The vertebral processes serve as attachment points for ligaments and back muscles. Vertebral processes - there are seven in total all projecting from the vertebral arch: one spinous process (posteroinferior), two transverse processes (posterolateral), and four articular processes.The vertebral canal is the space throughout the spinal column that is enclosed by the vertebral foramina. The pedicles, laminae, and body of each vertebra form a cavity (vertebral foramen). These facilitate the passage of spinal nerves from the spinal cord. The pedicles contain vertebral notches (superior, inferior) which form intervertebral foramina. It consists of two pedicles and two laminae. Vertebral arch - the structure located posterior to the body.Adjacent vertebral bodies are separated by intervertebral discs. Their size increases as one descends down the vertebral column. Vertebral body - the large cylindrical part located anteriorly that gives strength to the spine.However, they all have the following basic structure:
They vary in size and characteristics, especially from one region to the next. Mnemonic: A super simple way to remember the five regions of the vertebral column is to use the mnemonic ' Can This Little Servant Cook?' How many vertebrae do we have? The vertebral column consists of 33 vertebrae in total, divided as follows: In this article we’ll explore the anatomy and functions of the vertebral column. Segmental arteries and vertebral venous plexus (internal, external) Longitudinal (anterior, posterior), ligamenta flava, interspinous, supraspinous, nuchal, alar, cruciate ligament of atlas, costotransverse, ligaments of head of rib (intra-articular, radiate)Ĭervical lordosis, thoracic kyphosis, lumbar lordosis, sacral kyphosisįlexion, extension, lateral flexion, lateral extension, rotation Intervertebral discs, uncovertebral, zygapophyseal (facet), craniovertebral (atlanto-occipital, atlanto-axial), costovertebral, sacroiliac Vertebral body, vertebral arch (pedicles, lamina), vertebral processes (spinous, transverse, articular) Therefore, it’s important to take good care of it and maintain a good posture at all times! Key facts about the vertebral column RegionsĬervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, Sacral, Coccygeal Your vertebral column also protects your fragile spinal cord and helps support the weight of the upper body. Thanks to the spine, you can twist, bend and sway your trunk in almost any direction. The vertebral column is divided into five regions and consists of 33 vertebrae interlaced by strong joints and ligaments.Īlthough the spine can be a pain in the back, it’s function is very important. It is part of the axial skeleton and extends from the base of the skull to the tip of the coccyx. The vertebral column (spine or backbone) is a curved structure composed of bony vertebrae that are interconnected by cartilaginous intervertebral discs.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
